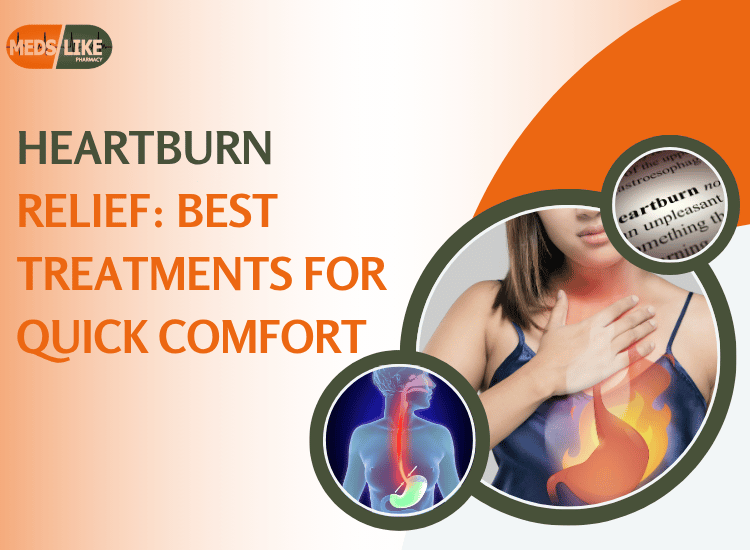
Heartburn is a common digestive condition that affects millions of people globally. Characterized by a burning sensation in the chest, often after meals or when lying down, heartburn is not just uncomfortable — it can also interfere with your daily life. While occasional heartburn is manageable, frequent symptoms may indicate an underlying condition like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Fortunately, both quick-acting remedies and long-term treatments are available to bring relief. This guide explores the most effective solutions — from immediate symptom relief to strategies for preventing chronic discomfort.
What Causes Heartburn?
Heartburn occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus — the tube that connects your mouth and stomach. This backflow, known as acid reflux, irritates the esophageal lining and causes that familiar burning feeling.
Common triggers include:
- Eating large or fatty meals
- Consuming spicy, acidic, or fried foods
- Lying down soon after eating
- Smoking or drinking alcohol
- Obesity or pregnancy
- Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs, aspirin)
Quick Relief for Heartburn
If you’re experiencing heartburn right now, fast-acting remedies can help soothe the burning sensation almost immediately.
1. Antacids
Antacids are the go-to solution for fast relief. These over-the-counter medications neutralize stomach acid and work within minutes.
Popular options:
- Tums
- Rolaids
- Maalox
- Mylanta
They’re best for occasional heartburn and should not be used excessively, as overuse can lead to side effects like diarrhea or kidney problems.
2. Baking Soda Water
A home remedy that can provide temporary relief is mixing half a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water. This alkaline solution neutralizes stomach acid.
Note: It should be used sparingly, as too much sodium bicarbonate can affect electrolyte balance.
3. Chewing Gum
Chewing sugar-free gum after meals can stimulate saliva production, which helps wash away acid and reduce its effect on the esophagus.
4. Licorice or DGL Supplements
Deglycyrrhizinated licorice (DGL) may help soothe the esophageal lining and reduce inflammation. Available in tablet or chewable form, it can offer natural relief for mild symptoms.
Long-Term Treatment for Chronic Heartburn
If heartburn occurs more than twice a week, you may need a longer-term approach. This includes medication, lifestyle adjustments, and in some cases, medical procedures.
1. H2 Blockers
H2 receptor blockers reduce acid production in the stomach and are useful for moderate, recurring heartburn.
Examples:
- Famotidine (Pepcid)
- Ranitidine (withdrawn in many countries due to safety concerns)
These drugs provide longer-lasting relief than antacids and can be taken before meals or at bedtime.
2. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs are among the most effective long-term medications for treating severe heartburn and GERD. They block acid production at the source and promote healing of the esophagus.
Common PPIs:
- Omeprazole (Prilosec)
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)
- Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
They’re best taken 30–60 minutes before a meal and should be used under medical supervision to avoid long-term side effects like nutrient deficiencies or bone fractures.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthier habits can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of heartburn.
Effective strategies include:
- Eating smaller meals: Avoid overloading the stomach.
- Avoid trigger foods: Spicy, acidic, fried, and fatty foods are common culprits.
- Stay upright after eating: Wait at least 2–3 hours before lying down.
- Elevate the head of your bed: This helps gravity prevent acid reflux at night.
- Lose excess weight: Extra belly fat increases abdominal pressure, worsening reflux.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol: Both relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing acid to rise.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can worsen acid reflux. Relaxation techniques like yoga, deep breathing, meditation, and regular exercise can improve digestion and reduce symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
While heartburn is often harmless, recurring symptoms may point to a more serious condition like GERD, esophagitis, or even Barrett’s esophagus — a precancerous change in the esophageal lining.
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Heartburn more than twice a week
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain not related to eating
- Unintentional weight loss
- Vomiting or black stools (signs of bleeding)
Your doctor may recommend an endoscopy or prescribe stronger medications to control acid production and protect the esophagus.
Natural Supplements and Alternatives
For those seeking alternatives to conventional medication, natural remedies and supplements may offer relief when used appropriately.
- Aloe vera juice (deacidified): Soothes irritation in the esophagus
- Slippery elm: Forms a protective coating in the digestive tract
- Apple cider vinegar: Some find that diluted ACV before meals improves digestion (use with caution and consult a professional)
Caution: Natural doesn’t always mean safe — consult your healthcare provider before using supplements, especially if you’re on medications.
Final Thoughts
Heartburn is uncomfortable, but it doesn’t have to take over your life. Whether you’re looking for quick fixes to soothe the burn or long-term strategies to prevent flare-ups, a combination of lifestyle adjustments and appropriate treatments can make a big difference.
Remember, persistent heartburn should never be ignored. Getting the right diagnosis and managing your symptoms early can prevent more serious complications down the road. Speak with your healthcare provider if your heartburn becomes frequent, severe, or unresponsive to treatment.
Your comfort matters — and with the right approach, lasting relief is within reach.