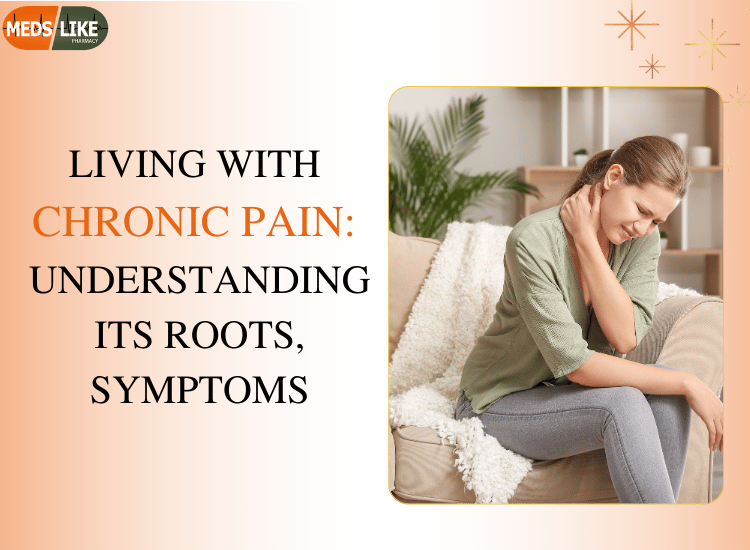
Chronic pain is a widespread yet often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike acute pain, which serves as a temporary warning signal of injury or illness, chronic pain persists for months or even years, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life. With the help of the carisoprodol-containing tablets Pain O Soma 350mg, you can get relief from neck and lower back pain.
Whether caused by an underlying medical condition, injury, or an unknown factor, chronic pain can take a toll on both physical and mental well-being. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for finding effective relief and improving daily life.
What is Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain is defined as pain that lasts for more than three months, persisting beyond the normal healing time of an injury or illness. It can be continuous or intermittent, mild or severe, and may affect any part of the body. Unlike acute pain, which typically subsides once the underlying issue is treated, chronic pain remains even after the apparent cause has healed.
Pain signals originate in the nervous system, and when they continue to fire over an extended period, they can alter the way pain is processed, making even minor discomfort feel more intense. This makes chronic pain a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management.
Common Causes of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can have a variety of causes, including injuries, diseases, or even unknown factors. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Injuries and Trauma
- Car accidents, falls, or sports injuries may cause nerve damage or lingering pain.
- Surgical procedures can sometimes lead to prolonged pain, even after recovery.
2. Medical Conditions
- Arthritis: Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis often result in chronic joint pain.
- Fibromyalgia: A condition that causes widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage, often seen in diabetes, can lead to chronic pain, numbness, or tingling sensations.
- Migraines: Chronic headaches and migraines can cause severe pain that disrupts daily life.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like lupus and multiple sclerosis can contribute to long-term pain.
3. Lifestyle Factors
- Poor posture, lack of exercise, or repetitive movements can lead to musculoskeletal pain.
- Chronic stress can increase muscle tension and inflammation, exacerbating pain conditions.
4. Unknown Causes
In some cases, chronic pain may develop without an obvious cause. This can make diagnosis and treatment challenging, leading to frustration for both patients and healthcare providers.
Symptoms of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain manifests in different ways, depending on the underlying cause and affected area. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent pain that may be dull, burning, throbbing, or sharp.
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion in affected joints or muscles.
- Fatigue and difficulty sleeping due to discomfort.
- Mood changes, such as anxiety, depression, and irritability.
- Sensitivity to touch or temperature changes in the affected area.
Chronic pain can also lead to a condition called central sensitization, where the nervous system becomes more sensitive to pain signals, making previously mild sensations feel more intense.
Pathways to Relief: Managing Chronic Pain
While pain can be challenging to treat, there are various methods to help manage and alleviate symptoms. A comprehensive pain management plan often involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and alternative therapies.
1. Medical Treatments
- Medications:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen) for mild cases.
- Prescription medications such as muscle relaxants, antidepressants, or nerve pain medications (e.g., gabapentin).
- Corticosteroid injections for inflammation-related pain.
- Opioids (used cautiously due to the risk of dependence).
- Physical Therapy:
- Targeted exercises and stretches to strengthen muscles and improve mobility.
- Posture correction and ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain.
- Surgical Interventions:
- In severe cases, procedures like nerve blocks, spinal cord stimulation, or joint replacement may be considered.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
- Exercise and Movement:
- Low-impact activities like yoga, swimming, or walking can improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Strength training helps support joints and relieve muscle tension.
- Healthy Diet:
- Anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish may help reduce pain.
- Staying hydrated and avoiding excessive processed foods can support overall health.
- Sleep Hygiene:
- Establishing a consistent sleep routine can improve rest and help manage pain levels.
- Using supportive pillows or mattresses can ease discomfort during sleep.
3. Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: Helps stimulate the nervous system and release pain-relieving chemicals.
- Massage Therapy: Eases muscle tension and promotes relaxation.
- Chiropractic Care: Can be beneficial for musculoskeletal-related pain.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like deep breathing and guided meditation help manage stress and pain perception.
4. Mental Health Support
Chronic pain not only affects the body but also takes a toll on mental health. Many individuals with pain experience anxiety, depression, or frustration. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor can be helpful in developing coping strategies. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in changing negative thought patterns associated with chronic pain.
5. Support Networks
Joining a pain support group—either in person or online—can provide emotional support and practical advice from others facing similar challenges. Having a strong support system of family and friends also plays a vital role in managing pain.
Conclusion
Living with chronic pain is a daily challenge, but with the right approach, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Identifying the underlying cause, adopting a comprehensive treatment plan, and making lifestyle changes can all contribute to long-term relief.
If you or a loved one is struggling with chronic pain, seeking professional medical advice is the first step toward finding an effective treatment plan. With persistence and the right support, those living with chronic pain can regain control over their health and well-being.